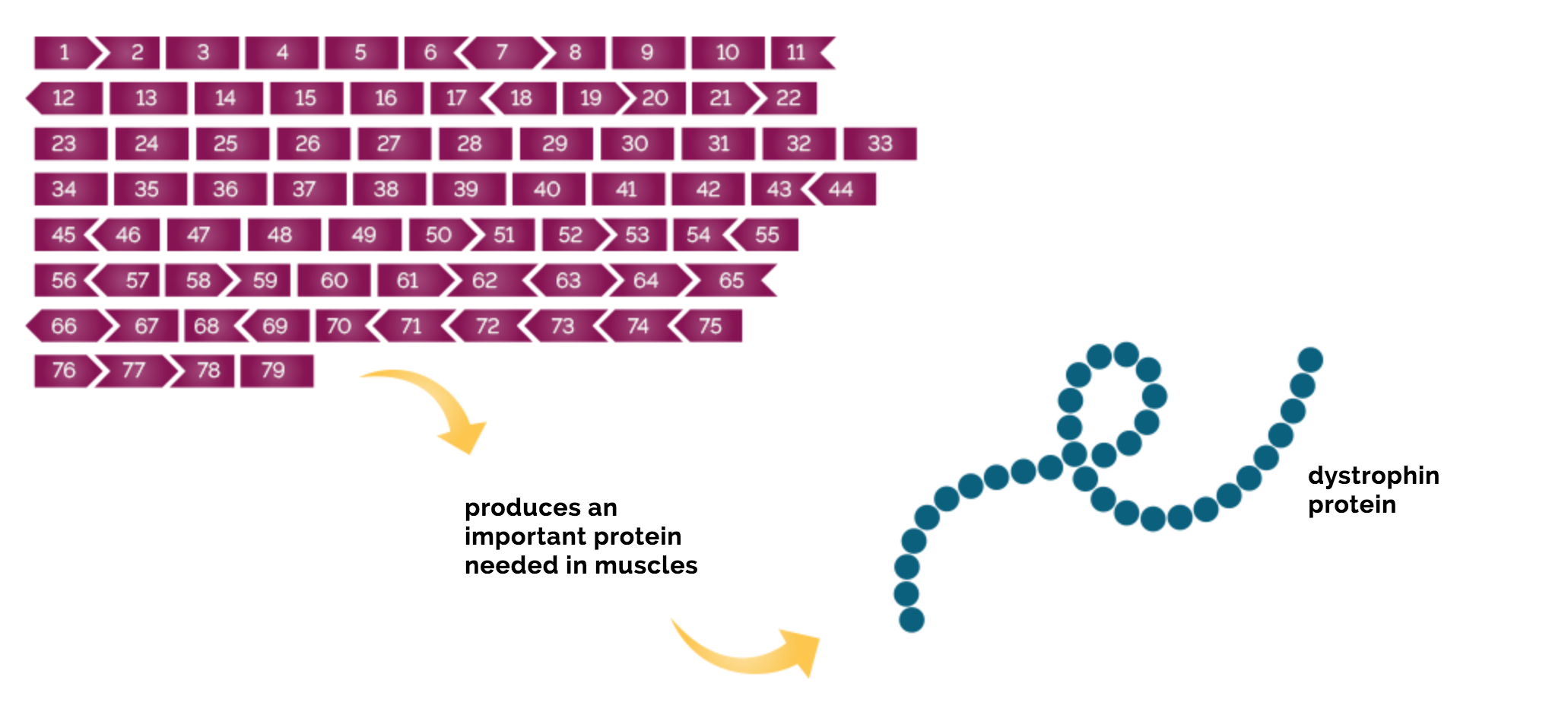
Dystrophin Protein Dmd
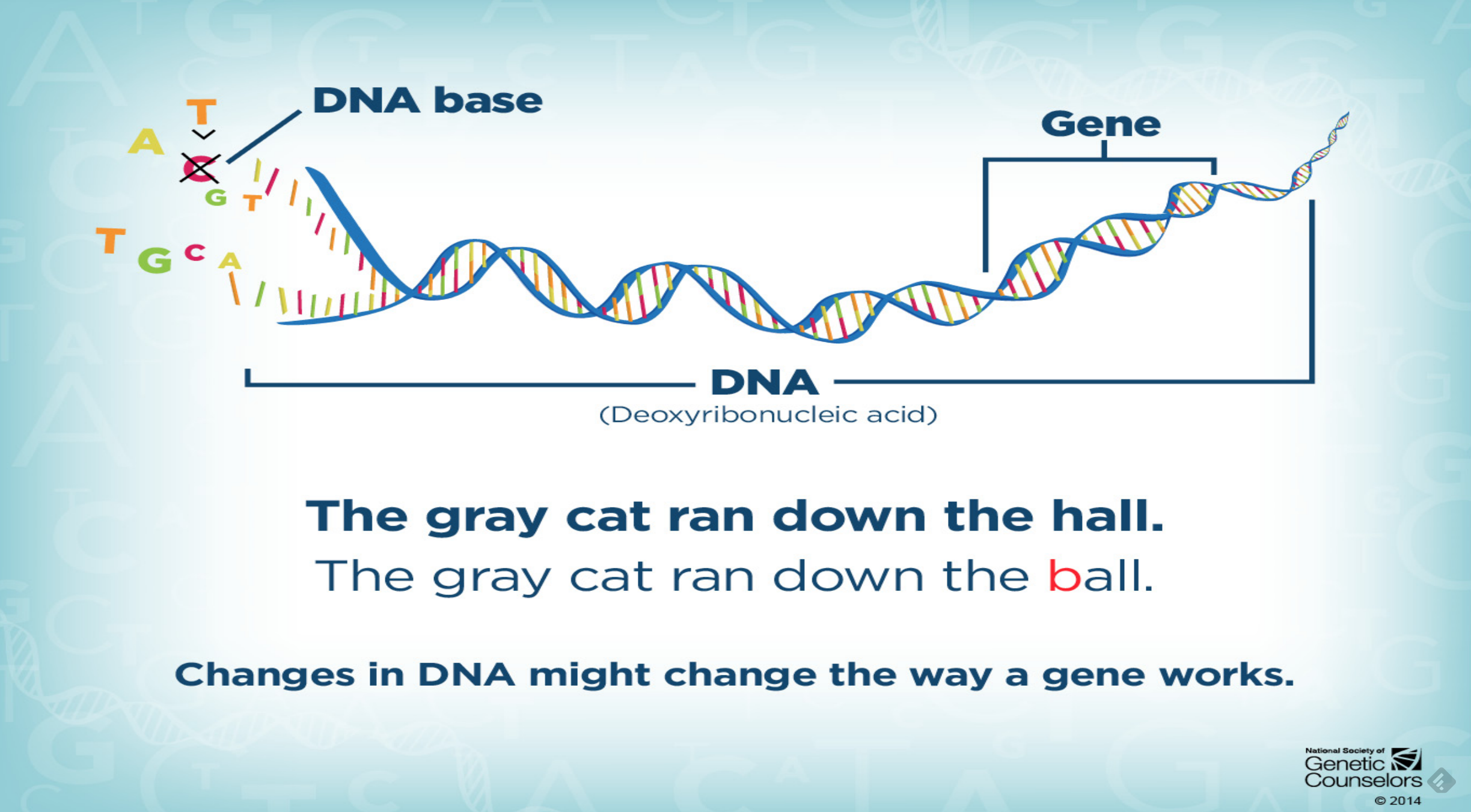
Exon skipping as a treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) Exon skipping is being heavily researched for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), where the muscular protein dystrophin is prematurely truncated, which leads to a nonfunctioning protein.
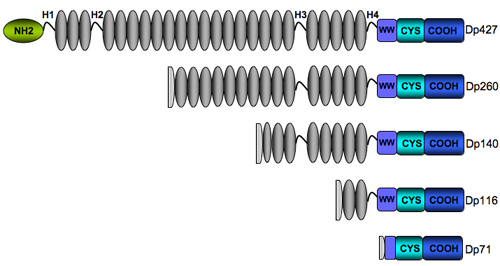
Dystrophin protein dmd. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is caused by deletion, duplication or point mutation of the dystrophin geneOf the 7 exons most commonly deleted, 49,50 and 51 aooear to be the hot spots Multiplex ligationdependent probe amplification test proved to be a powerful tool in detecting deletions/duplications and in some cases point mutations/polymorphisms along the DMD. Microdystrophin gene therapy robustly induces the production of a shorter, but functional, version of the dystrophin protein and reduces muscle damage in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients, according to preliminary results of a Phase 1/2 clinical trial DMD is a severe type of muscular dystrophy caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene This leads to the absence of the dystrophin. History and Background In 1860, French neurologist Guillaume Benjamin Amand Duchenne was the first to describe the disorder named after himself In 1986, researchers supported by the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) identified a gene linked to Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) on the X chromosome In 1987, the protein associated with this gene was identified, and named dystrophin.
The study did meet its primary biological endpoint of microdystrophin protein expression Patients receiving SRP9001 had mean microdystrophin expression of 281% as measured by western blot, at. SRP9001 uses a harmless adenoassociated virus to deliver a shorter version of the DMD gene to muscle cells Once inside the cell, the cell’s own molecular machinery “reads” the inserted gene and produces microdystrophin, a trimmeddown version of dystrophin, the protein missing in those with DMD. SRP9001 uses a harmless adenoassociated virus to deliver a shorter version of the DMD gene to muscle cells Once inside the cell, the cell’s own molecular machinery “reads” the inserted gene and produces microdystrophin, a trimmeddown version of dystrophin, the protein missing in those with DMD.
DMD (Dystrophin) is a Protein Coding gene Diseases associated with DMD include Muscular Dystrophy, Duchenne Type and Muscular Dystrophy, Becker Type Among its related pathways are Degradation of the extracellular matrix and Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Exon skipping as a treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) Exon skipping is being heavily researched for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), where the muscular protein dystrophin is prematurely truncated, which leads to a nonfunctioning protein. The identification of the DMD gene and dystrophin protein led to hopes for new therapeutic approaches that addressed the primary defect Intrinsic features of both the gene and protein slowed progress in translation of molecular understanding to effective therapeutics.
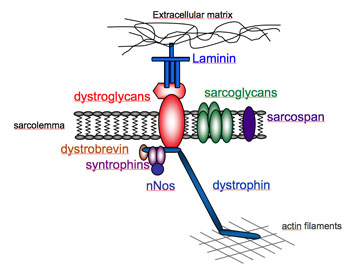
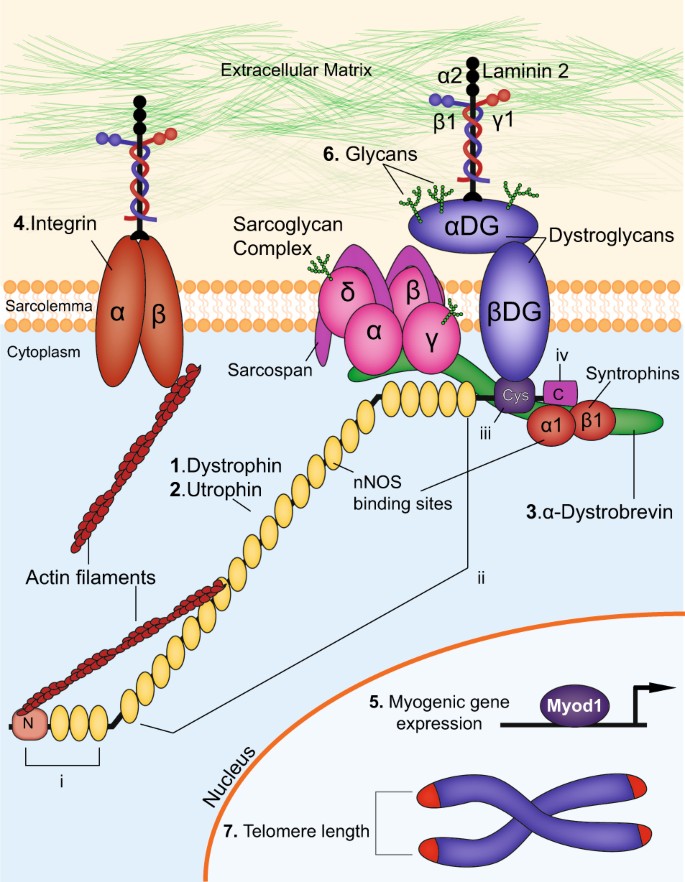
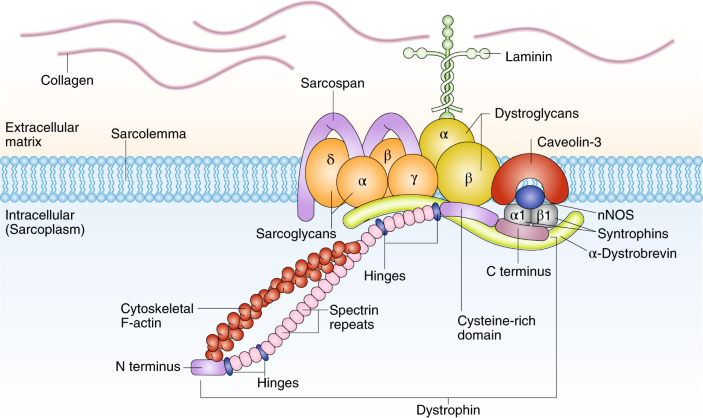
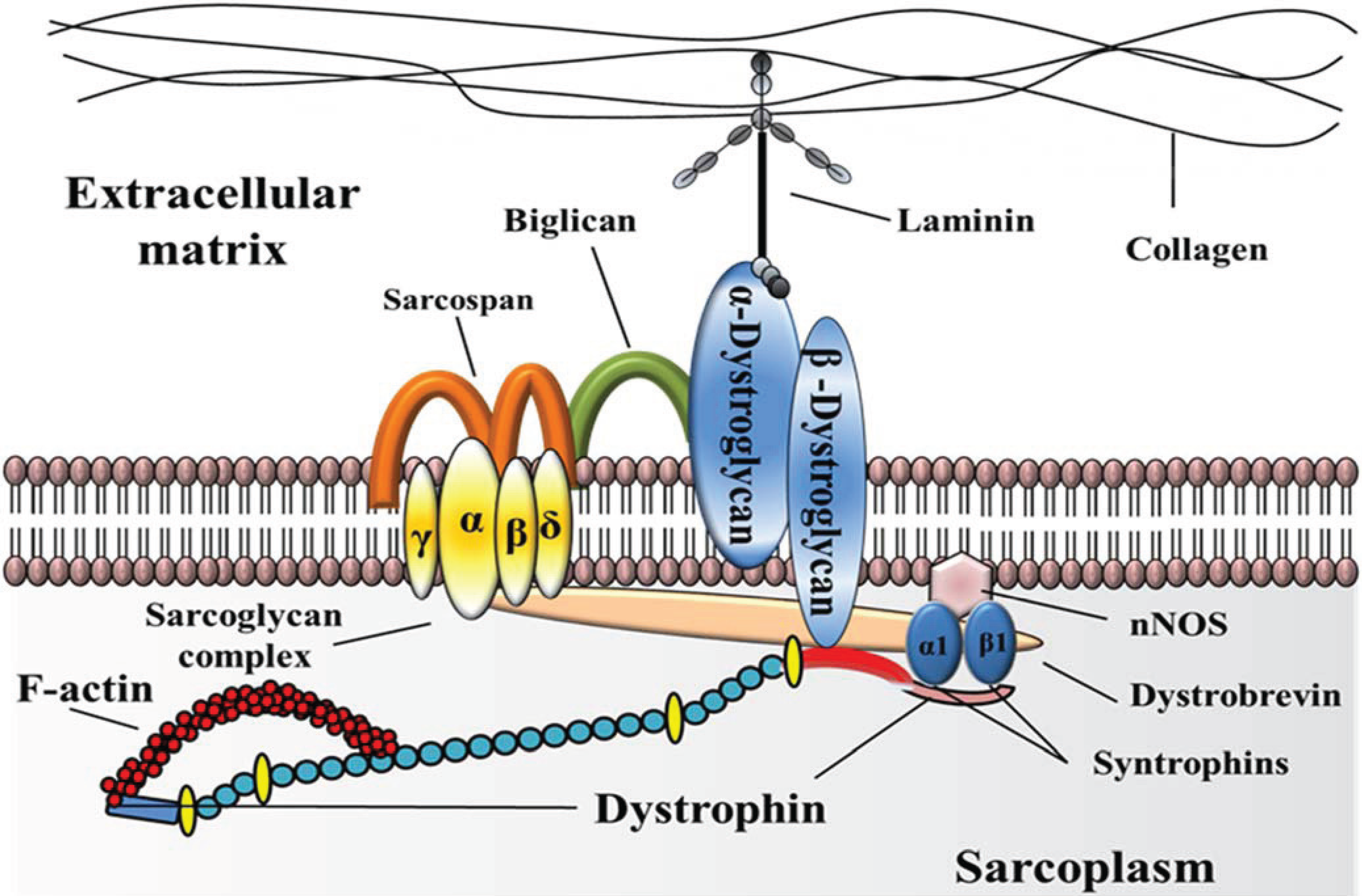
SRP9001 uses a harmless adenoassociated virus to deliver a shorter version of the DMD gene to muscle cells Once inside the cell, the cell’s own molecular machinery “reads” the inserted gene and produces microdystrophin, a trimmeddown version of dystrophin, the protein missing in those with DMD. Component of the dystrophinassociated glycoprotein complex which is composed of three subcomplexes a cytoplasmic complex comprised of DMD (or UTRN), DTNA and a number of syntrophins, such as SNTB1, SNTB2, SNTG1 and SNTG2, the transmembrane dystroglycan complex, and the sarcoglycansarcospan complex. DMD, the largest known human gene, provides instructions for making a protein called dystrophin This protein is located primarily in muscles used for movement (skeletal muscles) and in heart (cardiac) muscle Small amounts of dystrophin are present in nerve cells in the brain In skeletal and cardiac muscles, dystrophin is part of a group of proteins (a protein complex) that work together to strengthen muscle fibers and protect them from injury as muscles contract and relax.
It is associated with the triadic junctions in skeletal muscle and is therefore probably involved with calcium ion homeostasis The protein was also detected in smooth muscle of stomach. Produces internal deletions or duplicatons in protein Levels of dystrophin High (40% to 70%) Distal rod deletions (exons 45 48) Low (10% of normal) Nterminus deletions Clinical Phenotype Correlates with amount & function of dystrophin Effects of dystrophin mutations Other Dystrophin absence DMD phenotype Severe. DMD is an Xlinked recessive disorder caused by mutations in the DMD gene, which is responsible for producing the dystrophin protein Dystrophin is a key part of a protein complex that maintains muscle integrity during normal activity and exercise Mutations to the DMD gene prevent dystrophin protein production.
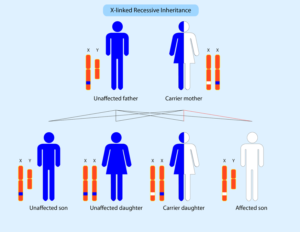
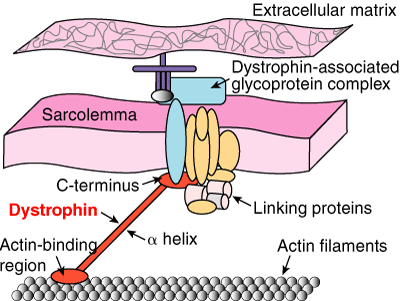
The role of the dystrophin complex and protein family in muscle and describes the physiological processes that are affected in Duchenne muscular dystrophy I INTRODUCTION Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe Xlinked recessive, progressive musclewasting disease affecting 1 in 3,500 boys (146) Patients are usually. Fulllength dystrophin is a large, rodshaped protein of 427 kDa composed of 3685 amino acid residues In skeletal muscle fibers, the protein localizes at the cytoplasmic face of the sarcolemma (Watkins et al), where it constitutes 5% of sarcolemmal protein and 0002% of total striated muscle protein (Hoffman et al). DMD is a devastating muscle disease that affects 1 in 5000 boys worldwide It is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene on the Xchromosome, which is why it only affects boys It is the most severe as well as the most common form of muscular dystrophy Affected boys become symptomatic and are diagnosed around 25 years of age.
At 12 weeks compared to baseline, the study met its primary biological endpoint of microdystrophin protein expression with mean microdystrophin expression of 281%, as measured by western blot. Duchenne MD happens because of a lack of dystrophin (disTROfin), a protein made by the muscle cells In DMD, a variation or missing part of the dystrophin gene causes a loss of the dystrophin protein This protein loss prevents the muscle fibers from working properly, leading to weakness. DMD is caused by the absence of the dystrophin protein Dystrophin is a large protein that provides multiple cellular functions and helps to protect skeletal and cardiac muscle against injury.
DMD is caused by the changes of mutations in the gene that helps make dystrophin The dystrophin causes the muscles to become weaker The DNA of person with Duchenne does not code for the protein dystrophin at all. Also known as Xlinked dilated cardiomyopathy (XLCM). DMD pathophysiology and therapy Myofiber membrane cytoskeleton The identification of dystrophin nucleated the study of the membrane cytoskeleton of The transition to therapy The identification of the DMD gene and dystrophin protein led to hopes for new therapeutic Becker muscular dystrophy.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a genetic disorder characterized by progressive muscle degeneration and weakness due to the alterations of a protein called dystrophin that helps keep muscle cells intact DMD is one of four conditions known as dystrophinopathies. The dystrophin protein Dystrophin is a rodshaped protein, measuring about 150 nm, consisting of 3684 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 427 kDa Dystrophin is predominantly hydrophilic throughout its entire length and 31% of the aminoacids are charged (ie Arg, Asp, Glu, His and Lys). The study did meet its primary biological endpoint of microdystrophin protein expression Patients receiving SRP9001 had mean microdystrophin expression of 281% as measured by western blot, at.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a genetic disease characterized by progressive muscle weakness, is present at birth in people who have the condition In people with Duchenne, the muscles lack a. The protein, called dystrophin, is about 400 kD in size and represents about 0002% of total striated muscle protein;. Component of the dystrophinassociated glycoprotein complex which accumulates at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and at a variety of synapses in the peripheral and central nervous systems and has a structural function in stabilizing the sarcolemma Also implicated in signaling events and synaptic transmissionBy similarity 1 Publication.
Now, the fact that both Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy result from mutations in the same dystrophin gene means that they are “allelic disorders,” and when a mutation occurs in dystrophin that’s severe enough to result in no protein at all, for example a nonsense or a frameshift mutation, the result is Duchenne muscular dystrophy. DMD is caused by the absence of the dystrophin protein Dystrophin is a large protein that provides multiple cellular functions and helps to protect skeletal and cardiac muscle against injury. About Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a rare, fatal neuromuscular genetic disease that occurs in approximately one in every 3,5005,000 males worldwide DMD is caused by a change or mutation in the gene that encodes instructions for dystrophin Symptoms of DMD usually appear in infants and toddlers.
The study did meet its primary biological endpoint of microdystrophin protein expression Patients receiving SRP9001 had mean microdystrophin expression of 281% as measured by western blot, at. History and Background In 1860, French neurologist Guillaume Benjamin Amand Duchenne was the first to describe the disorder named after himself In 1986, researchers supported by the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) identified a gene linked to Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) on the X chromosome In 1987, the protein associated with this gene was identified, and named dystrophin. Dystrophin is a 427 kilodalton protein that constitutes 001% of total muscle protein and 5% of the sarcolemmal cytoskeletal proteins Dystrophin is localized in the inner aspect of the sarcolemma, and is abundant at the myotendinous junction and at the postsynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction.
The encoded protein forms a component of the dystrophinglycoprotein complex (DGC), which bridges the inner cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix Deletions, duplications, and point mutations at this gene locus may cause Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD), or cardiomyopathy. Now, the fact that both Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy result from mutations in the same dystrophin gene means that they are “allelic disorders,” and when a mutation occurs in dystrophin that’s severe enough to result in no protein at all, for example a nonsense or a frameshift mutation, the result is Duchenne muscular dystrophy. DMD is caused by the absence of the dystrophin protein Dystrophin is a large protein that provides multiple cellular functions and helps to protect skeletal and cardiac muscle against injury.
DMD is caused by the absence of the dystrophin protein Dystrophin is a large protein that provides multiple cellular functions and helps to protect skeletal and cardiac muscle against injury. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a genetic, Xlinked, musclewasting disorder that affects –5000 boys and is caused by mutations in the DMD gene The mutations found in DMD patients disrupt the open reading frame of the gene resulting in the inability to produce the protein dystrophin The lack of dystrophin triggers progressive muscle degeneration, leading to loss of muscle. Protein DMD_HUMAN Dystrophin FUNCTION Anchors the extracellular matrix to the cytoskeleton via Factin Ligand for dystroglycan Component of the dystrophin associated glycoprotein complex which accumulates at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and at a variety of synapses in the peripheral and central nervous systems and has a structural.
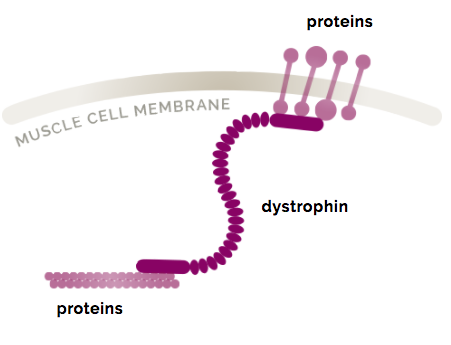
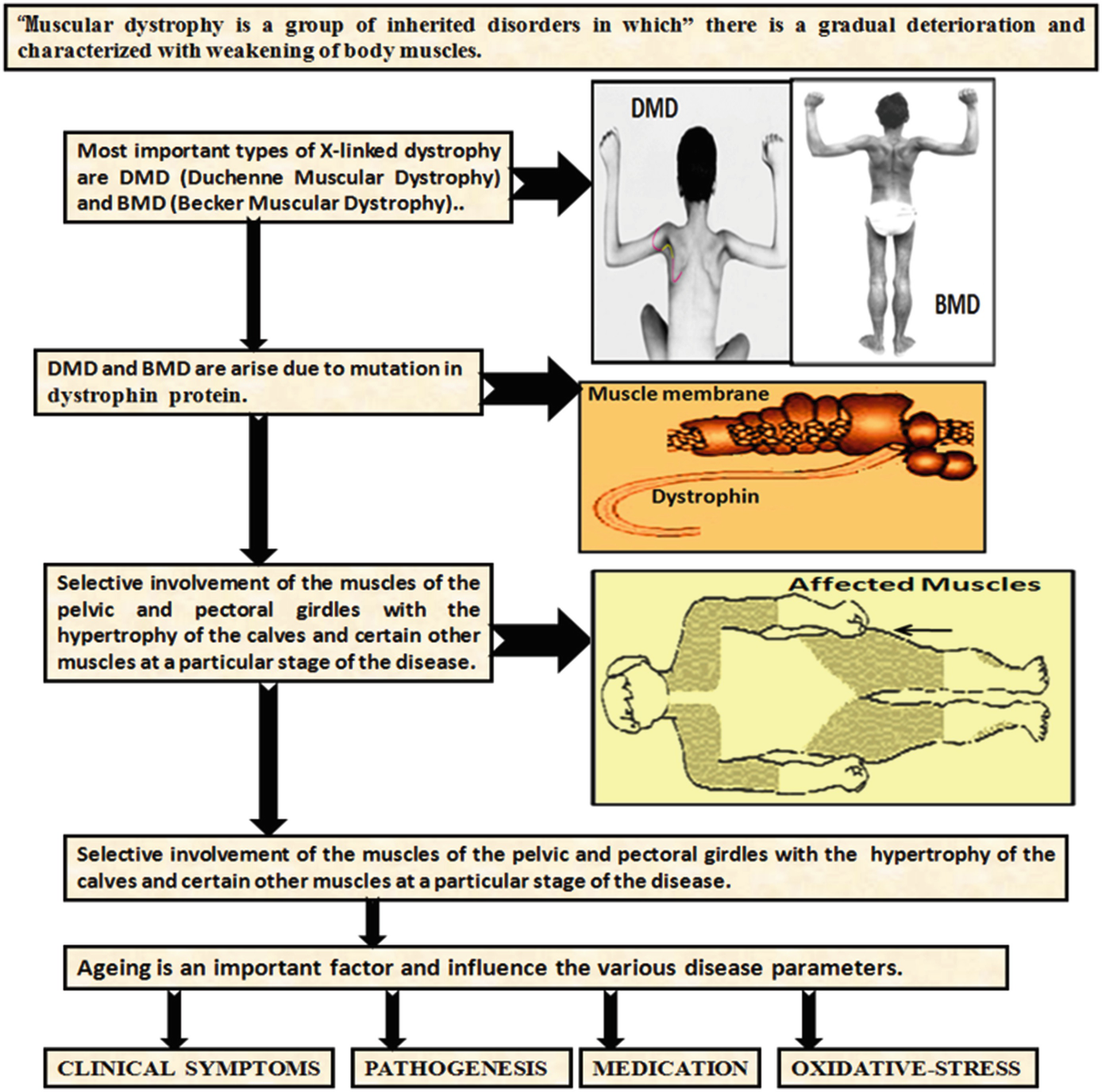
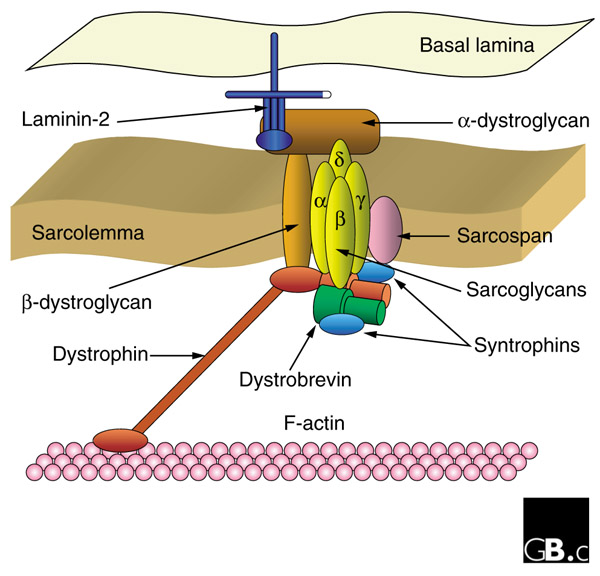
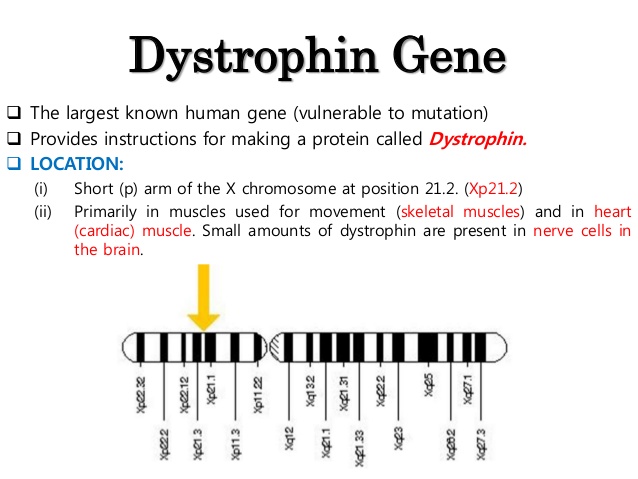
DMD is inherited in a Xlinked recessive manner DMD is caused by a mutation of the dystrophin gene at locus Xp21, located on the short arm of the X chromosome Dystrophin is responsible for connecting the cytoskeleton of each muscle fiber to the underlying basal lamina (extracellular matrix), through a protein complex containing many subunits. Nance explains that DMD is caused by deletions, duplications, point mutations or premature stop codons in the gene that makes dystrophin, a protein that stabilizes muscle cell membranes and supports the contractile apparatus Without this protein, damage builds up over time, leading to muscle scarring, inflammation and eventually atrophy. Dystrophin the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus The protein product of the human Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus (DMD) and its mouse homolog (mDMD) have been identified by using polyclonal antibodies directed against fusion proteins containing two distinct regions of the mDMD cDNA.
History and Background In 1860, French neurologist Guillaume Benjamin Amand Duchenne was the first to describe the disorder named after himself In 1986, researchers supported by the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) identified a gene linked to Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) on the X chromosome In 1987, the protein associated with this gene was identified, and named dystrophin. The dystrophinassociated complex Fulllength dystrophin is a large, rodshaped protein of 427 kDa composed of 3685 amino acid residues In skeletal muscle fibers, the protein localizes at the cytoplasmic face of the sarcolemma (Watkins et al), where it constitutes 5% of sarcolemmal protein and 0002% of total striated muscle protein (Hoffman et al). Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), one of the most severe forms of muscular dystrophy, is caused by a defect in the dystrophin gene The protein that this gene encodes is responsible for anchoring muscle cells’ inner frameworks, or cytoskeletons, to proteins and other molecules outside these cells, the extracellular matrix.
About Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a rare, fatal neuromuscular genetic disease that occurs in approximately one in every 3,5005,000 males worldwide DMD is caused by a change or mutation in the gene that encodes instructions for dystrophin Symptoms of DMD usually appear in infants and toddlers. Produces internal deletions or duplicatons in protein Levels of dystrophin High (40% to 70%) Distal rod deletions (exons 45 48) Low (10% of normal) Nterminus deletions Clinical Phenotype Correlates with amount & function of dystrophin Effects of dystrophin mutations Other Dystrophin absence DMD phenotype Severe. DMD is a muscle wasting disease caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene It is a progressive disease that usually causes death in early adulthood, with serious complications that include heart or respiratoryrelated problems It mostly affects boys, about 1 in every 3,500 or 5,000 male children.
DMD gene that encodes a 427kDa cytoskeletal protein called dystrophin The vast majority of DMD mutations result in the complete absence of dystrophin, whereas the presence of low levels of a truncated protein is seen in BMD patients In addition to these diseases, mutations in the genes encoding many components of the dystrophin. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is most often caused by frameshift mutations due to deletions of one or more exons from the dystrophin gene 2 The exons following the deletion are misaligned or “out of frame,” preventing translation of a functional dystrophin protein 2. Defects in DMD are the cause of Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) MIM BMD resembles DMD in hereditary and clinical features but is later in onset and more benign Defects in DMD are a cause of cardiomyopathy dilated Xlinked type 3B (CMD3B) MIM3045;.
Buy AntiDystrophin (DMD) (Marker of Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone, item number AB from Abeomics at Biomol!. The study did meet its primary biological endpoint of microdystrophin protein expression Patients receiving SRP9001 had mean microdystrophin expression of 281% as measured by western blot, at. This gene spans a genomic range of greater than 2 Mb and encodes a large protein containing an Nterminal actinbinding domain and multiple spectrin repeats The encoded protein forms a component of the dystrophinglycoprotein complex (DGC), which bridges the inner cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix.
About Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a rare, fatal neuromuscular genetic disease that occurs in approximately one in every 3,5005,000 males worldwide DMD is caused by a change or mutation in the gene that encodes instructions for dystrophin Symptoms of DMD usually appear in infants and toddlers. Exon skipping is being heavily researched for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), where the muscular protein dystrophin is prematurely truncated, which leads to a nonfunctioning protein Successful treatment by way of exon skipping could lead to a mostly functional dystrophin protein,. Dystrophin is a 427 kilodalton protein that constitutes 001% of total muscle protein and 5% of the sarcolemmal cytoskeletal proteins Dystrophin is localized in the inner aspect of the sarcolemma, and is abundant at the myotendinous junction and at the postsynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction.

Figure 1 From Gene Therapies That Restore Dystrophin Expression For The Treatment Of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Semantic Scholar

Humane Genetica

Inherited Disorders Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Practice Khan Academy
Dystrophin Protein Dmd のギャラリー
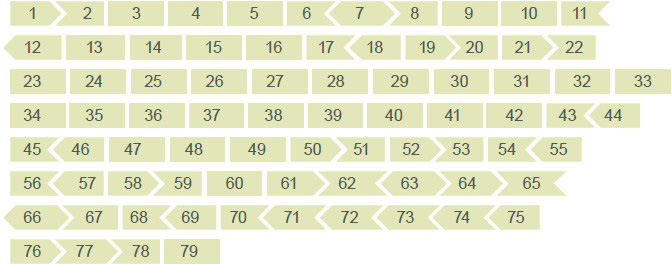
Types Of Mutations Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy
Dystrophin Isoforms And Their Expression
The Role Of Dystrophin In Duchenne Duchenne Com

Dmd Recombinant Protein Dystrophin Dmd Recombinant Protein Np 2

Humane Genetica

Dystrophin Protein Exon Skipping
The Dmd Mutations Database The Dystrophin Protein

The Role Of Dystrophin In Muscle Function Exondys 51 Eteplirsen Injection

Dmd Gene Genecards Dmd Protein Dmd Antibody

The Importance Of Genetic Diagnosis For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Journal Of Medical Genetics

What Is Exon Skipping And How Does It Work Muscular Dystrophy Uk

Solved Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dmd Is An X Linked R Chegg Com

Quest Article Exon Skipping In Dmd What Is It And Whom Can It Help Muscular Dystrophy Association

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy And Becker Muscular Dystrophy Pediatrics Merck Manuals Professional Edition
Genetic Causes Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy
What Is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Parent Project Md

Figure 1 From Genome Editing Gene Therapy For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Semantic Scholar
Humanizing The Mdx Mouse Model Of Dmd The Long And The Short Of It Npj Regenerative Medicine

Therapeutic Developments For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Nature Reviews Neurology X Mol
The Role Of Dystrophin In Duchenne Duchenne Com

Dystrophin Associated Protein An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Correction Of Diverse Muscular Dystrophy Mutations In Human Engineered Heart Muscle By Single Site Genome Editing Science Advances
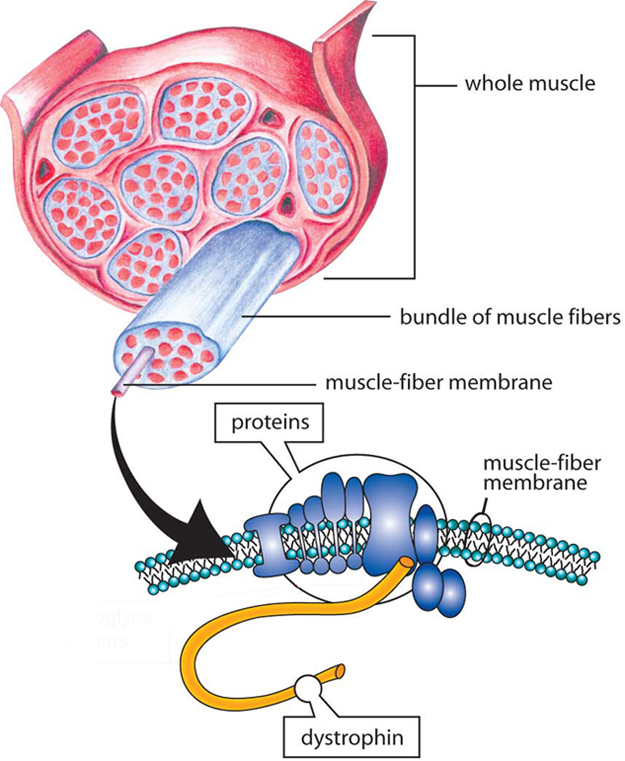
Diseases Dmd Causes Inheritance Muscular Dystrophy Association

Immune Response To Full Length Dystrophin Delivered To Dmd Muscle By A High Capacity Adenoviral Vector Molecular Therapy

Exondys 51 Eteplirsen For The Treatment Of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dmd Clinical Trials Arena
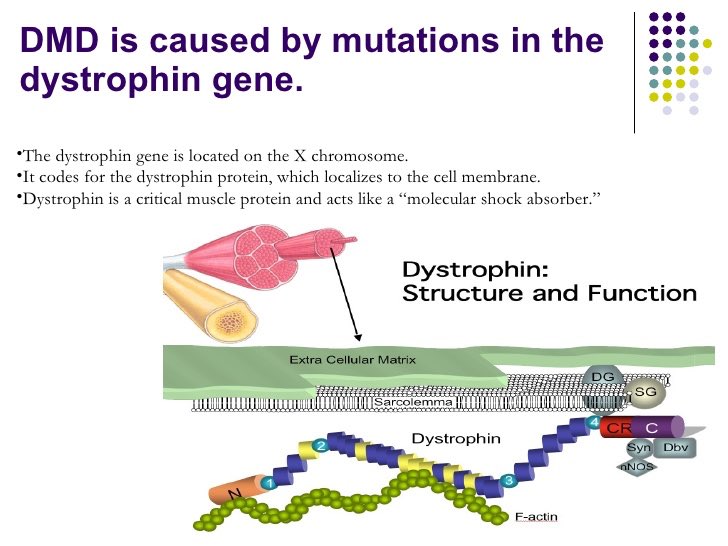
Doctorofmedicine Duchenne S Muscular Dystrophy Dmd Is Cause By Missing Protein Dystrophin

Restoring Dystrophin Expression In Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Muscle Progress In Exon Skipping And Stop Codon Read Through Sciencedirect

Dystrophin Is Required For The Formation Of Stable Muscle Attachments In The Zebrafish Embryo Development

Dystrophin

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Genetics Duchenne Com
Plos One Use Of Capillary Western Immunoassay Wes For Quantification Of Dystrophin Levels In Skeletal Muscle Of Healthy Controls And Individuals With Becker And Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy

Engineering Multiple U7snrna Constructs To Induce Single And Multiexon Skipping For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Molecular Therapy
Mouse Dmd Dystrophin Protein Recombinant His 3059 3314 Lsbio
Human Dystrophin Dmd Protein Myc Dykddddk Recombinant Abin

The Importance Of Genetic Diagnosis For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Journal Of Medical Genetics

Dystrophin Associated Muscular Dystrophies Learning From Genetics To Guide Therapeutics Almontashiri Na J Musculoskelet Surg Res
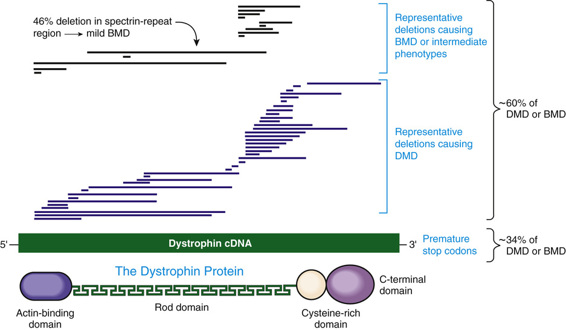
Of Structural Proteins Basicmedical Key
Aging Influence On Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dmd And Becker Muscular Dystrophy Bmd Springerlink

Corrective Therapies Solid Biosciences

Prime Global Medical Communications Agency

Crispr Helps Heal Mice With Muscular Dystrophy Science as
Confluence Mobile Crbs Confluence Wiki

The Role Of Dystrophin In Muscle Function Exondys 51 Eteplirsen Injection
Plos One Correlation Of Utrophin Levels With The Dystrophin Protein Complex And Muscle Fibre Regeneration In Duchenne And Becker Muscular Dystrophy Muscle Biopsies
The Dmd Mutations Database The Dystrophin Protein

Dmd Gene Therapy And Dystrophin Mutations In Animal Models A The Download Scientific Diagram

Dystrophin The Stem Cellar

Progress In Therapy For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Fairclough 11 Experimental Physiology Wiley Online Library

What Is Exon Skipping And How Does It Work Muscular Dystrophy Uk
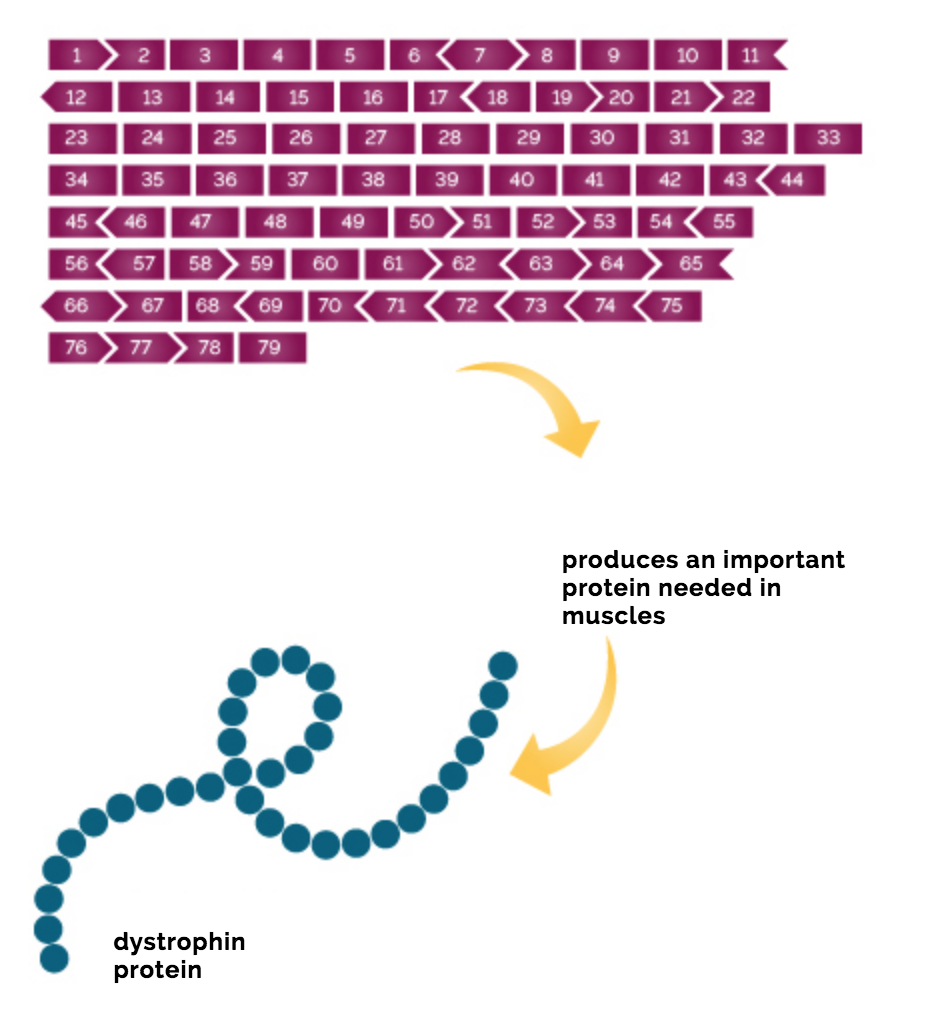
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Genetics Duchenne Com
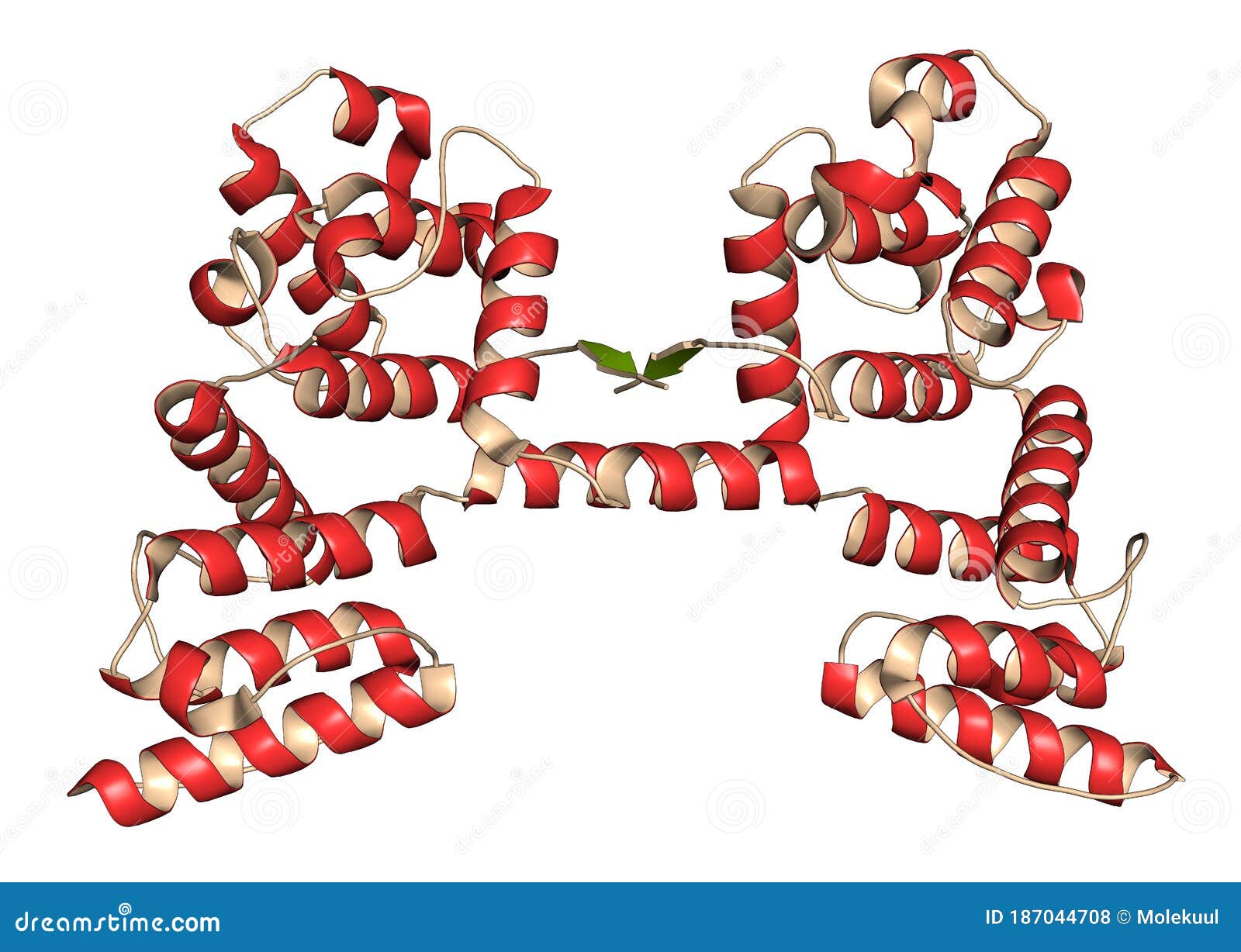
Dystrophin Muscle Protein Domain N Terminal Actin Binding Domain Defects Cause Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dmd Stock Illustration Illustration Of Myopathy Costamere

Animal Models Of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy From Basic Mechanisms To Gene Therapy Disease Models Mechanisms
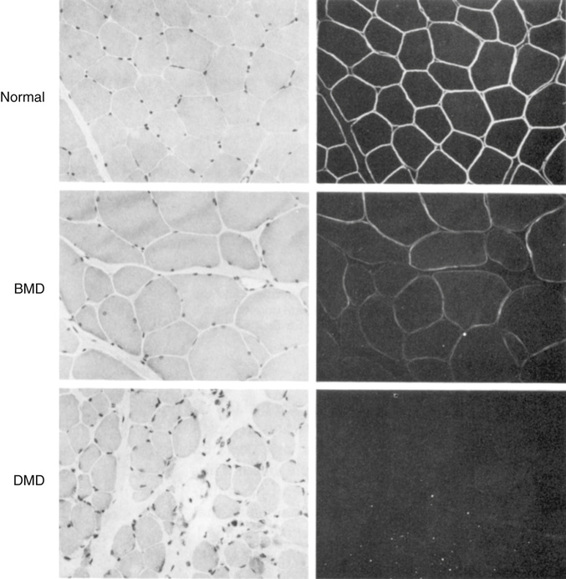
Of Structural Proteins Basicmedical Key
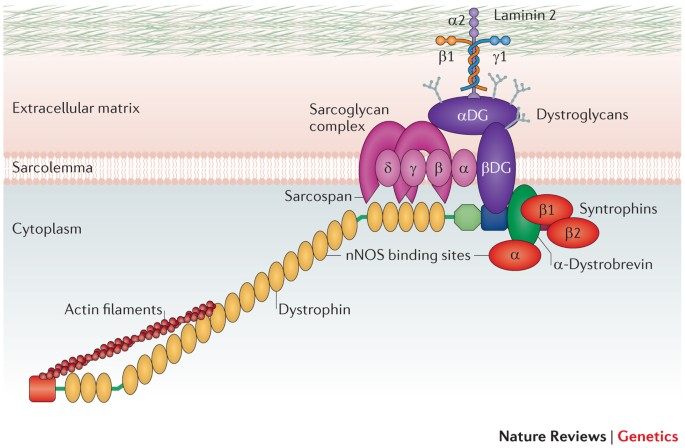
Therapy For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Renewed Optimism From Genetic Approaches Nature Reviews Genetics
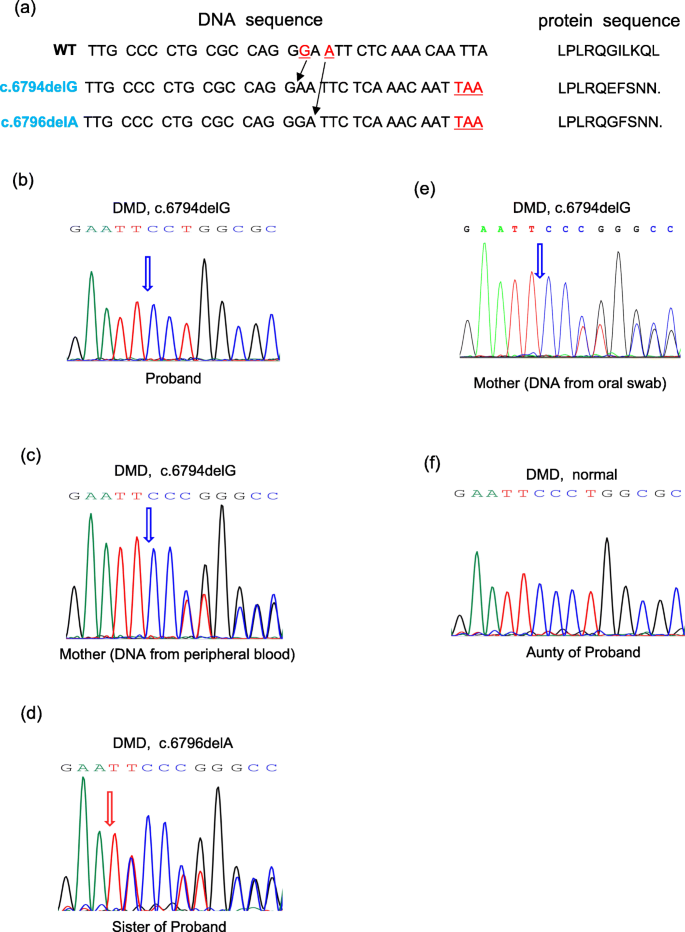
Prenatal Diagnosis Of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Revealed A Novel Mosaic Mutation In Dystrophin Gene A Case Report Bmc Medical Genetics Full Text

Biotech Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy

What Causes Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dmd Everyday Health

References In Local Restoration Of Dystrophin Expression With The Morpholino Oligomer Avi 4658 In Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy A Single Blind Placebo Controlled Dose Escalation Proof Of Concept Study The Lancet Neurology

Dmd Dystrophin Protein Dp Isoforms The Dmd Dystrophin Gene Download Scientific Diagram
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Neurology Update

Srpt Ex992 9 Htm

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Pediatrics Orthobullets

Dystrophin Wikipedia
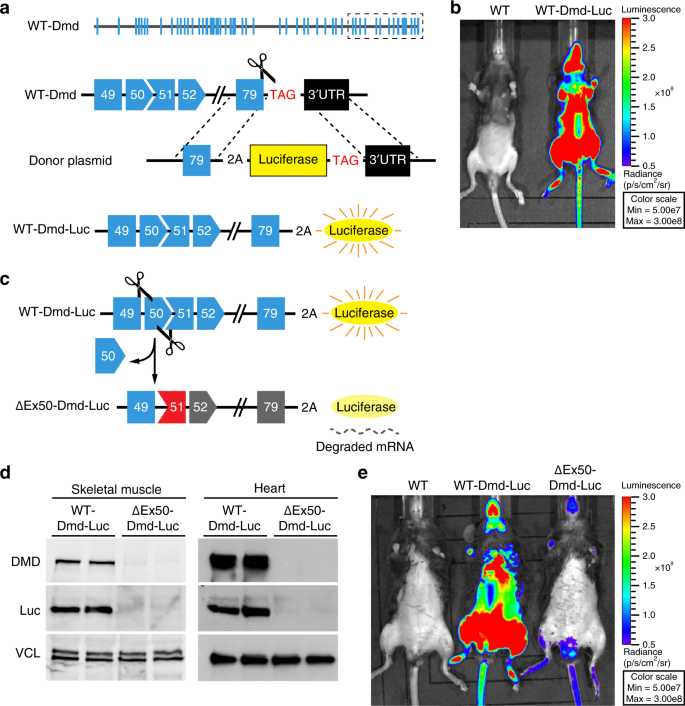
In Vivo Non Invasive Monitoring Of Dystrophin Correction In A New Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Reporter Mouse Nature Communications
Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text X Linked Dilated Cardiomyopathy A Cardiospecific Phenotype Of Dystrophinopathy Html

Gene Editing Restores Dystrophin Expression In A Canine Model Of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Science
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Genetics Duchenne Com

Efficient Restoration Of The Dystrophin Gene Reading Frame And Protein Structure In Dmd Myoblasts Using The Cindel Method Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids

While You Were Away Gene Editing Treats Mice With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy The Stem Cellar

The Protein Dystrophin Is Super Important For Stabilizing The Muscle Cell Membrane Mutations In Cell Membrane Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophies

Dystrophin Antibody Dmd 3244 Neobiotechnologies
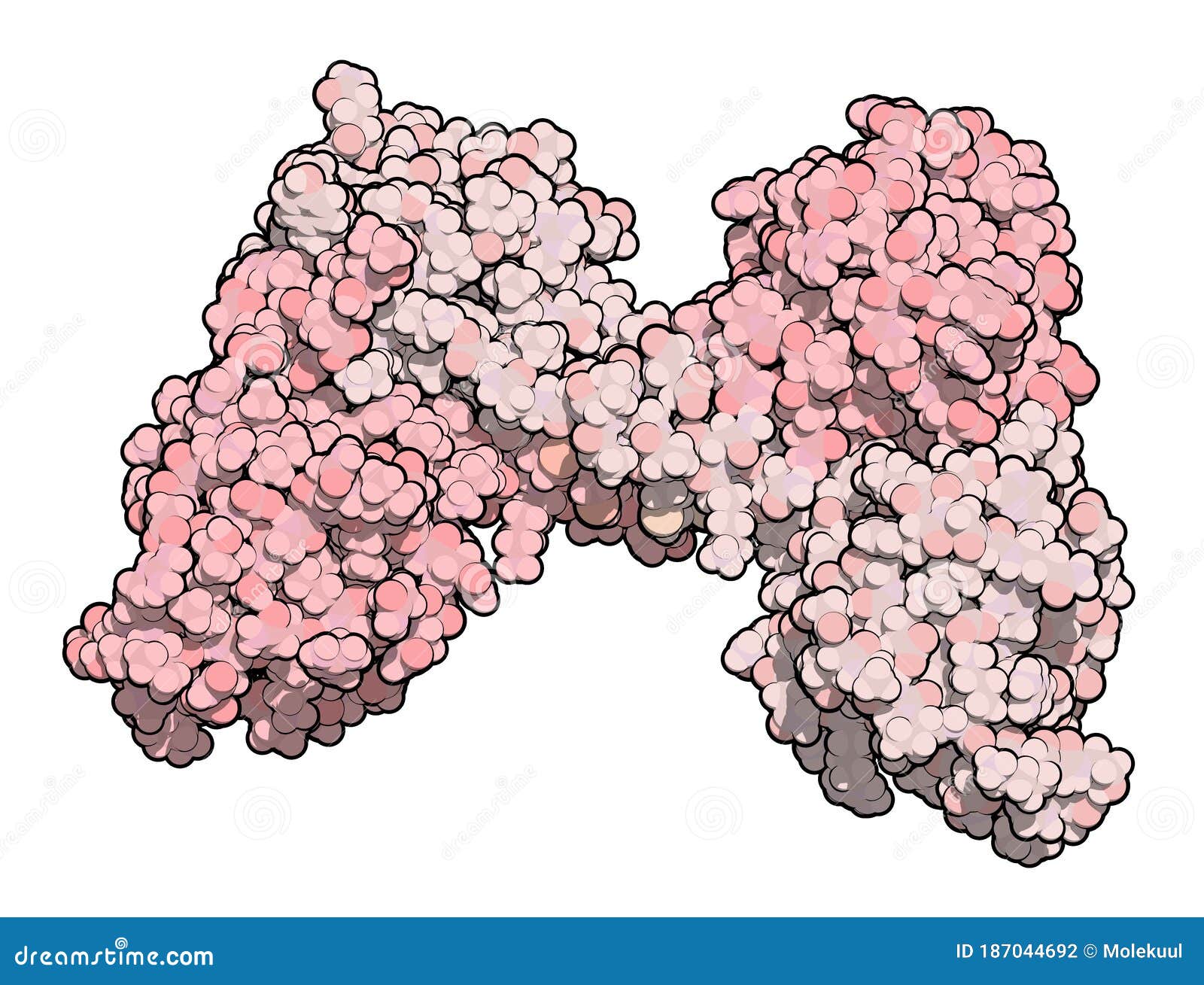
Dystrophin Muscle Protein Domain N Terminal Actin Binding Domain Defects Cause Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dmd Stock Illustration Illustration Of Muscle Duchene

Function And Genetics Of Dystrophin And Dystrophin Related Proteins In Muscle Physiological Reviews
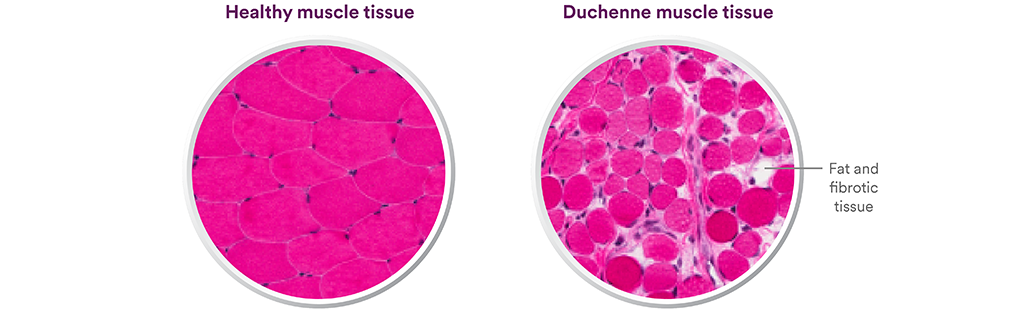
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dmd Sarepta Therapeutics

Orthogonal Analysis Of Dystrophin Protein And Mrna As A Surrogate Outcome For Drug Development Biomarkers In Medicine

Progress And Challenges In v Mediated Gene Therapy For Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Intechopen
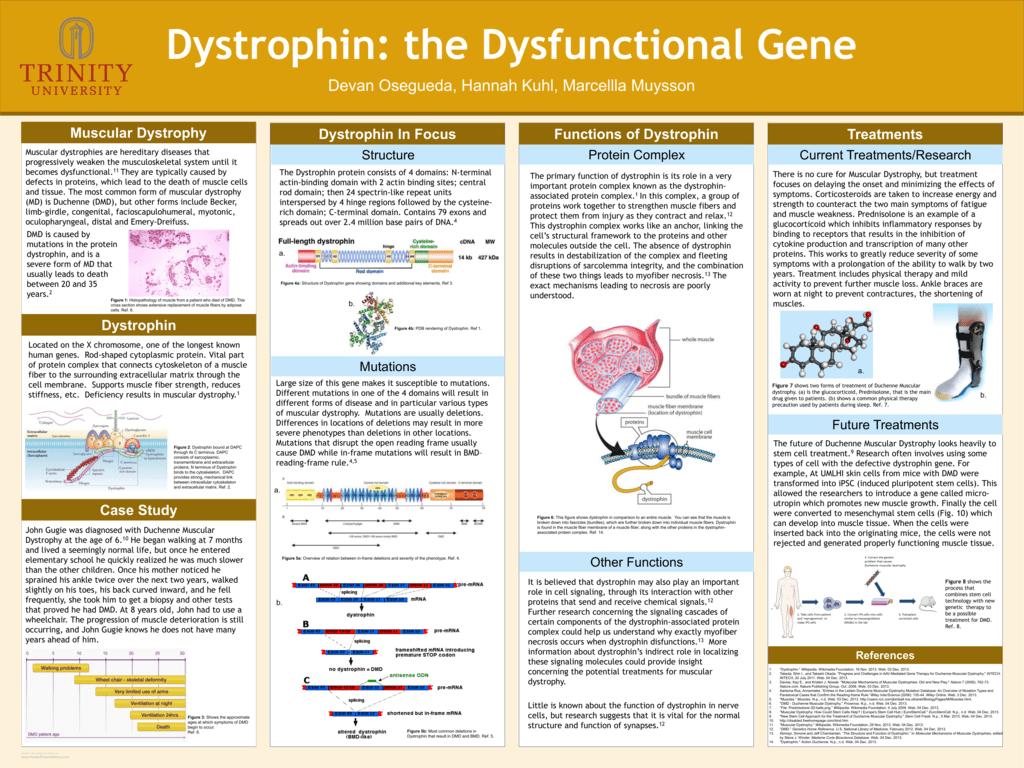
Dystrophin The Dysfunctional Gene

Viltepso Viltolarsen For The Treatment Of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
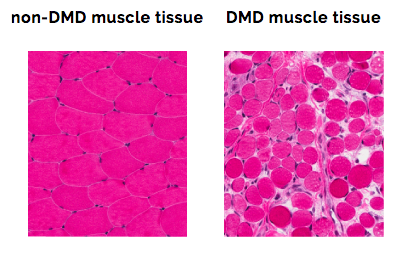
The Role Of Dystrophin In Duchenne Duchenne Com

Dystrophin Wikipedia
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Awaits Gene Therapy Nature Biotechnology
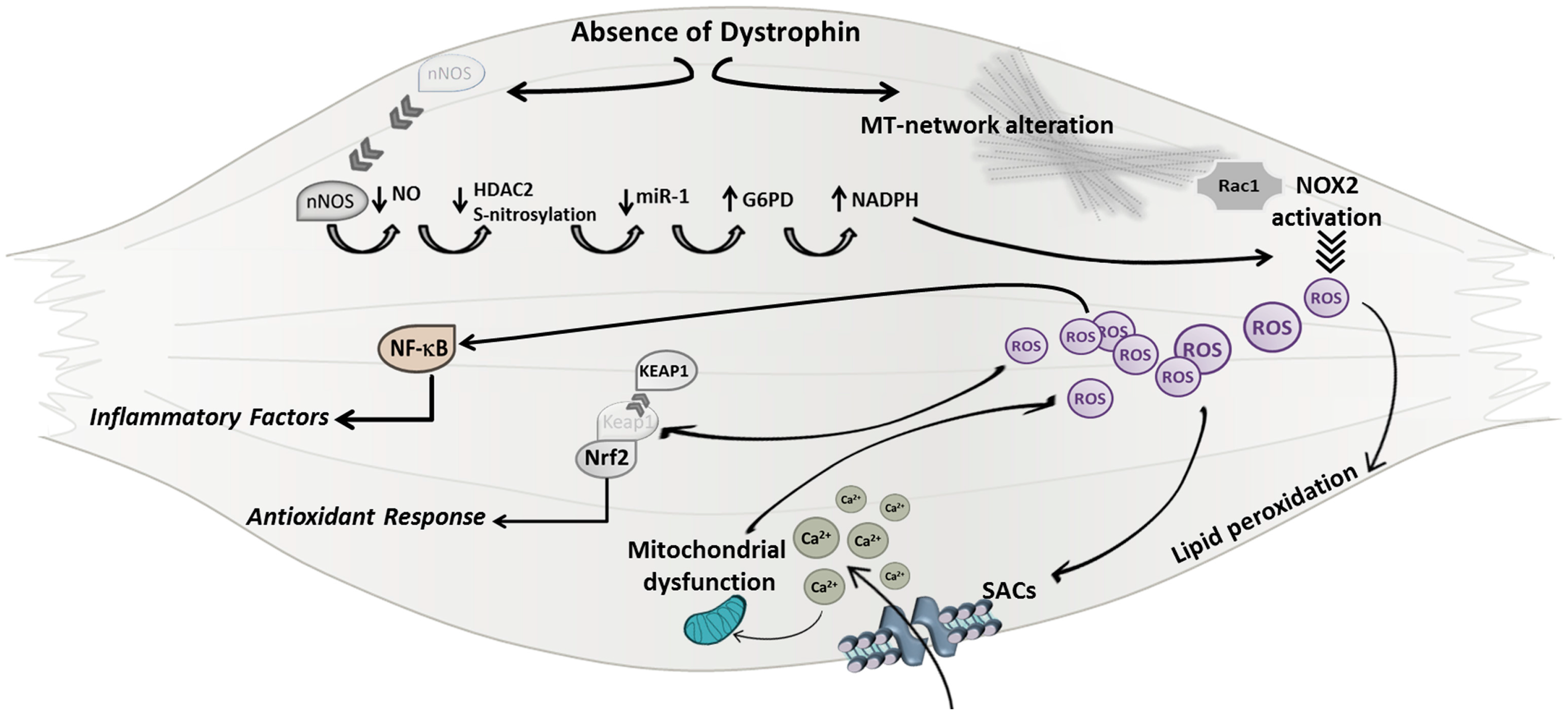
Jfmk Free Full Text Insights Into The Pathogenic Secondary Symptoms Caused By The Primary Loss Of Dystrophin Html

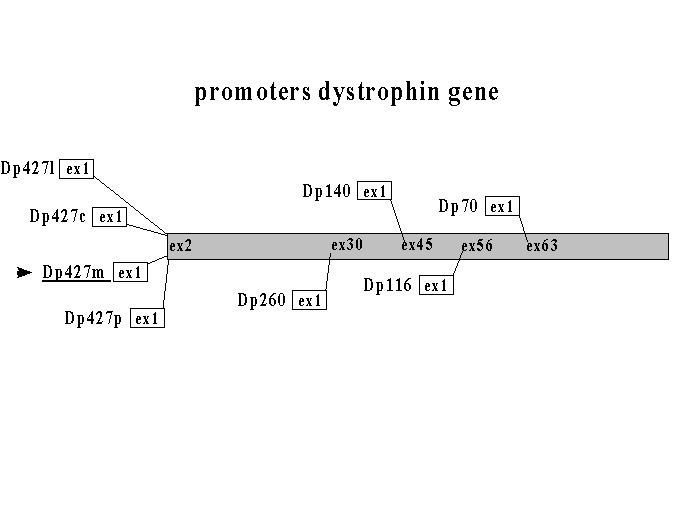
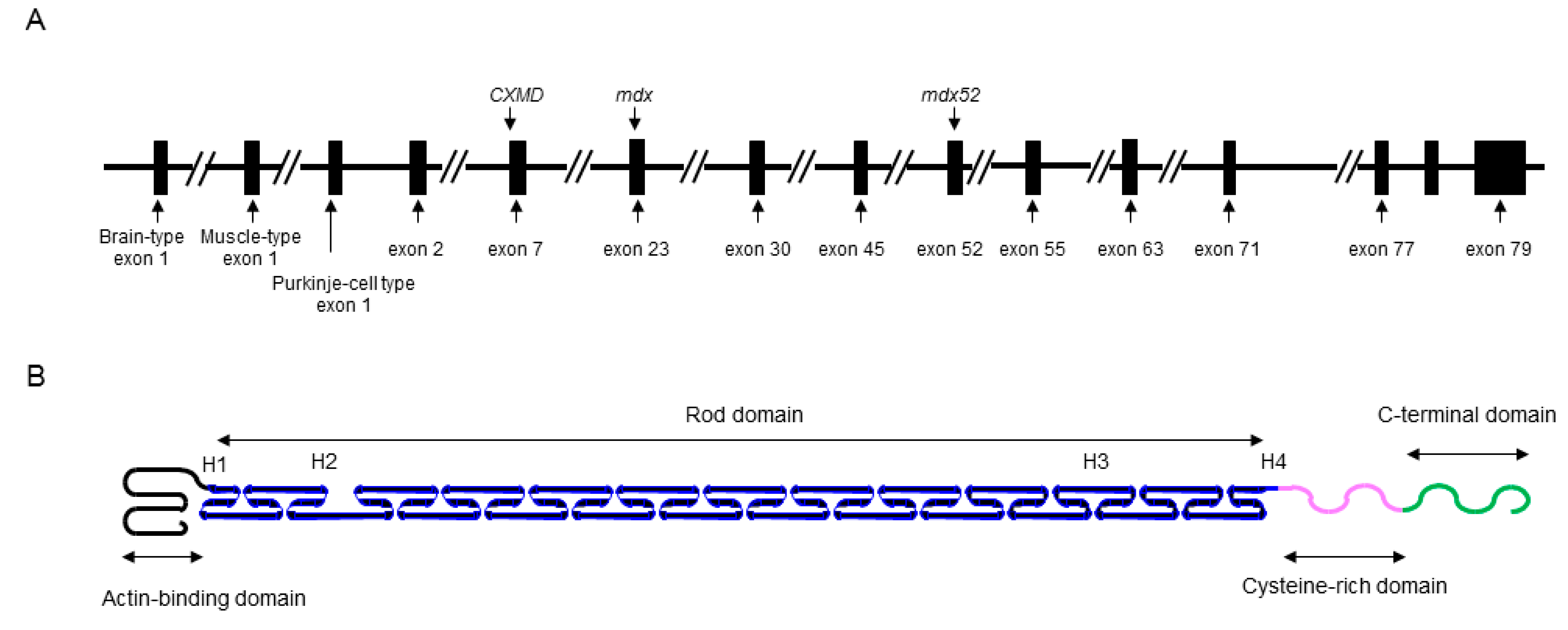
Structure Of The Dmd Gene Including Positions Of Promoters For Download Scientific Diagram

Dmd Gene Genecards Dmd Protein Dmd Antibody

Schematic Showing The Organization Of The Human Duchenne Muscular Download Scientific Diagram

The Canine Dystrophin Protein Ensembl Protein Id Enscafp Download Scientific Diagram
Why Is Inheritance Of Dystrophin Gene Not Studied Under Mendelian Inheritance Of Characters What Is The Cellular Process For Production Of Dystrophin And What Actually Is The Problem In Muscles Of People
Biology Free Full Text High Throughput Screening In Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy From Drug Discovery To Functional Genomics Html
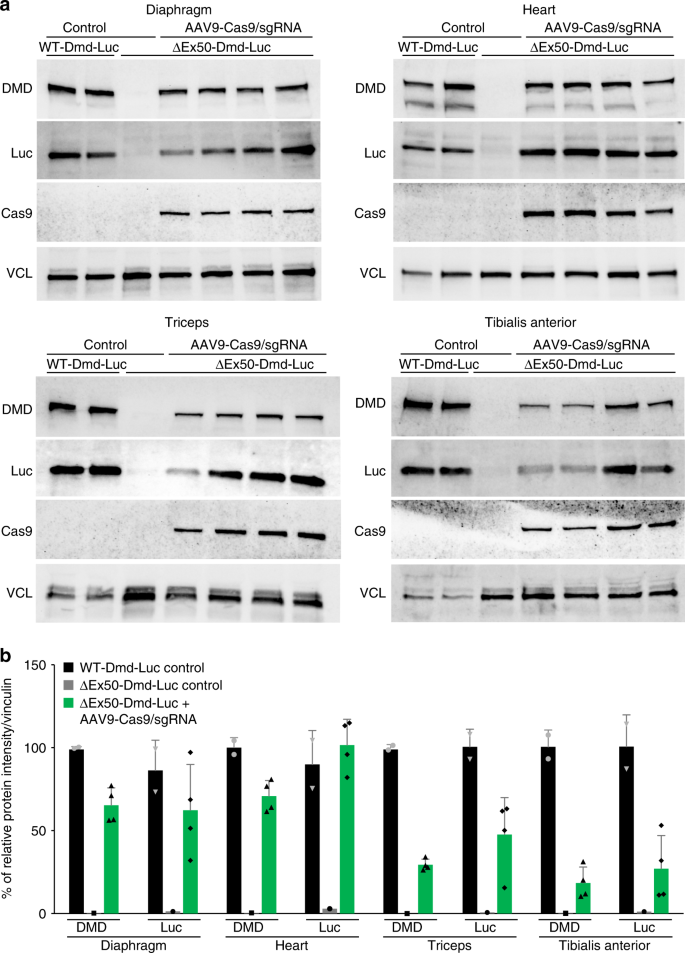
In Vivo Non Invasive Monitoring Of Dystrophin Correction In A New Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Reporter Mouse Nature Communications
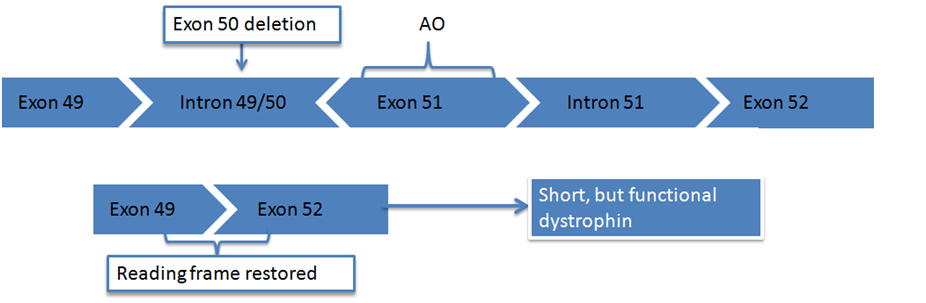
Exon Skipping Action Duchenne
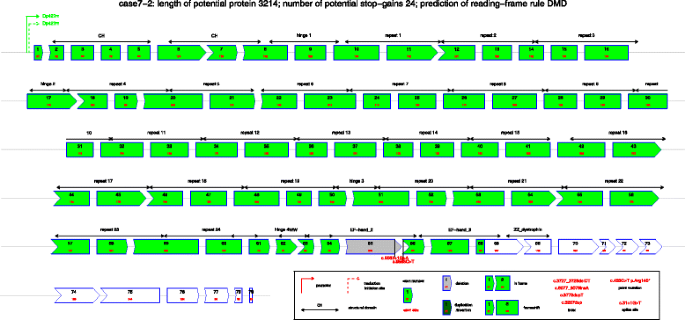
Dmdtoolkit A Tool For Visualizing The Mutated Dystrophin Protein And Predicting The Clinical Severity In Dmd Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text

Disease Resources Sarepta Therapeutics

References In Dystrophin And Mutations One Gene Several Proteins Multiple Phenotypes The Lancet Neurology

Infographic Treating Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy With Crispr The Scientist Magazine
Plos One Correlation Of Utrophin Levels With The Dystrophin Protein Complex And Muscle Fibre Regeneration In Duchenne And Becker Muscular Dystrophy Muscle Biopsies

Dmd Gene Genecards Dmd Protein Dmd Antibody



